MicroAlign doubles fibre array channels with nanometer accuracy

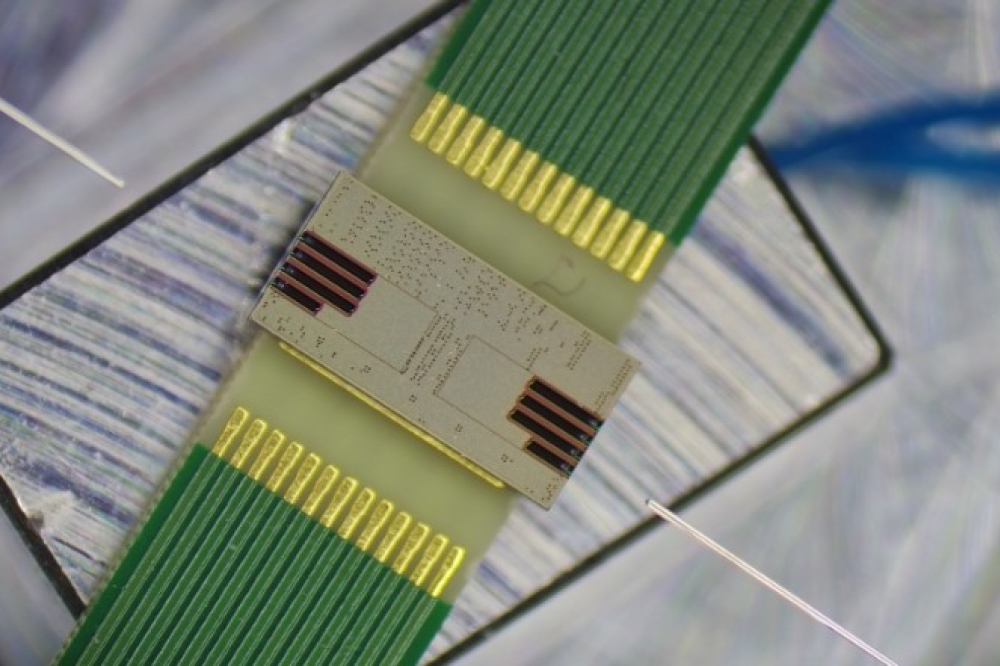
MicroAlign, a leading manufacturer of high-precision optical fibre arrays, has achieved a significant milestone in fibre-to-photonic chip connectivity. The company has successfully scaled its fibre arrays from 12 to 24 channels while maintaining 100-nanometer fibre-core pitch accuracy, setting a new benchmark for ultra-low-loss coupling in quantum photonic computing.
Efficient fibre-to-chip coupling is critical for advancing quantum photonic systems, where even minor misalignments can result in substantial optical losses. Traditional V-groove-based fibre arrays typically achieve core position accuracy around 0.5 µm, which is insufficient for next-generation quantum photonic applications. MicroAlign’s active alignment approach ensures that each fibre core is precisely positioned during manufacturing, enabling simultaneous, closed-loop alignment of all fibres without compromising accuracy.
“Every bit of optical energy is precious in high-end photonic applications. Maintaining a rapid pace of innovation is crucial to meet industry demands,” said Simone Cardarelli, CEO of MicroAlign. Marco Fattori, CTO, added: “Our technology allows us to manufacture high-channel-count fibre arrays without sacrificing core position accuracy, a step forward for scalable photonic integration.”
MicroAlign will present its findings at the SPIE Photonics West Conference in January 2026, showcasing the potential of active alignment fibre arrays to enable more efficient and scalable photonic systems.