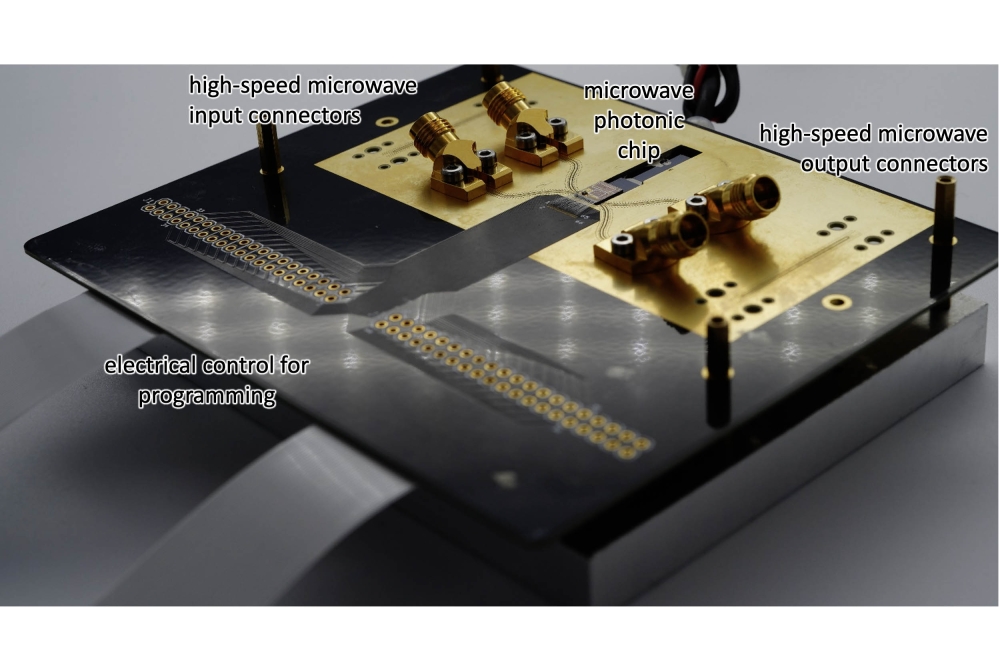
Vodafone and ORCA partner on modelling networks with quantum

By running Vodafone’s software on ORCA Computing’s PT-2 Series photonic quantum system, the companies aim to enhance techniques for finding optimal network layouts, potentially maximising speed and minimising required engineering work
Vodafone and ORCA Computing have announced a collaboration to explore the use of quantum technology in identifying the fastest and most cost-effective routes for upgrading and extending fixed and mobile broadband connections to more customers.
Quantum computing has the potential to handle more complex processing tasks than a traditional computer when planning, installing, and optimising large mobile radio and gigabit broadband networks.
As the size and complexity of networks grow alongside demand for new digital services, Vodafone is collaborating with ORCA Computing with the goal of enhancing current mathematical methods used to approximate optimal network layouts. Vodafone’s software will be run on ORCA Computing’s quantum computer – the ORCA PT-2 Series photonic quantum system. The solutions generated by the quantum system could, for example, help reduce total cable length and optimise the location of mobile base stations to maximise speed and minimise major civil engineering work.
Vodafone plans to initially assess ORCA’s quantum technology for solving complex optical fibre cable design challenges. Over time, the company says it expects to use quantum principles more widely when modelling its global network which spans more than 200 destinations, including an undersea cable network transporting around one sixth of the world’s internet traffic, and a new direct-to-mobile broadband satellite communications system.
The partnership with ORCA Computing, headquartered in the UK and with offices in Canada and the US, aims to support Vodafone’s strategy to enhance and extend its networks using greater automation and powerful new computing technologies. The company anticipates that quantum computing will improve the accuracy of network optimisation, as well as accelerate the use of machine learning and AI to predict faults before they impact customers.
“Our work with ORCA Computing aims to solve ultra-complex problems which otherwise would take many hours, weeks and even years to process on today’s classical computers,” said Luke Ibbetson, head of research and development at Vodafone. “Modelling new networks that maximise speed, reliability and coverage for customers, while navigating urban clutter and rural obstacles, could in future take minutes.”
James Fletcher, head of solutions architecture at ORCA Computing, added: “ORCA Computing’s continued collaboration with the Vodafone team marks an important step toward achieving practical and commercial quantum advantage. We have shown that quantum acceleration of telecommunications use cases is not just a theoretical concept, it’s a viable, deployable and commercially compelling solution.”