Improved on-chip integration of single-photon sources
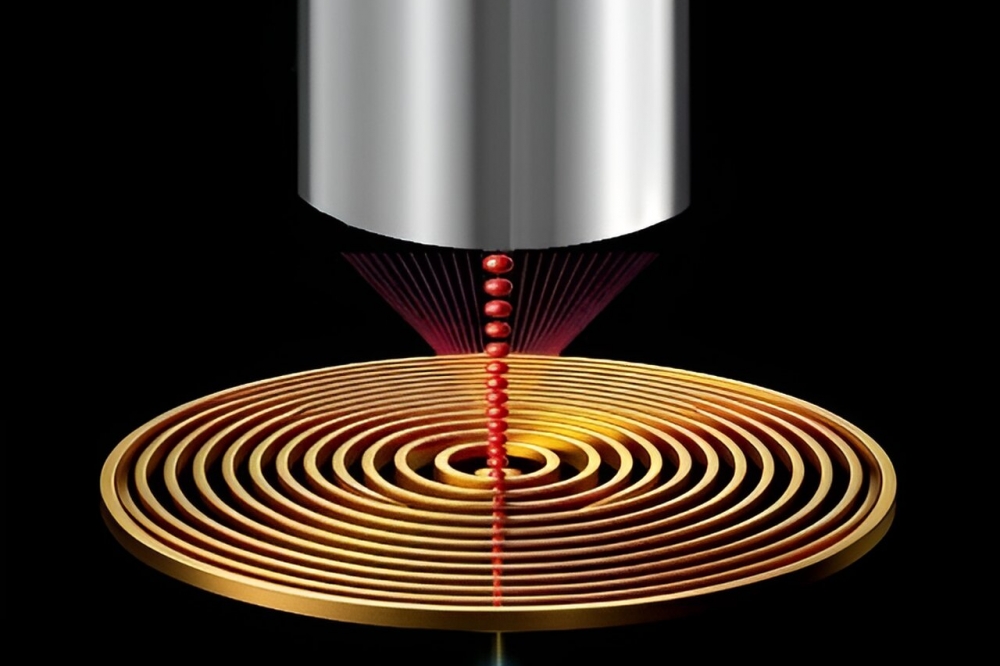
Using a novel antenna design, researchers have achieved high photon collection efficiencies for devices containing two different types of single-photon sources, representing a step forward for quantum technologies
Researchers from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have reported a significant advancement toward the on-chip integration of single-photon sources at room temperature. Describing their results in a paper in the journal Nano Letters, the scientists say that this achievement represents a substantial step forward in the field of quantum photonics and holds promise for various applications including quantum computing, cryptography, and sensing.
According to the researchers, the key innovation lies in the implementation of a hybrid metal–dielectric bullseye antenna, which delivers exceptional photon directionality. This novel antenna design allows for the efficient back-excitation of photons by placing the emitter within a subwavelength hole positioned at the centre of the antenna. This configuration enables both direct back-excitation and highly efficient front coupling of emission to low numerical aperture optics or optical fibres.
The study, which was conducted in collaboration with teams from Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) in the USA and from Ulm University in Germany, demonstrates the versatility of this concept by fabricating devices containing either colloidal quantum dots or nanodiamonds containing silicon-vacancy centres. Both these sources are excellent single-photon emitters even at room temperature. They were accurately positioned using two distinct nanopositioning methods.
The researchers report that both types of back-excited devices exhibited front collection efficiencies of approximately 70 percent at numerical apertures as low as 0.5. This means that, even with very simple and compact optical elements, most of the photons can be collected into the desired channel, and emitted photons can be accurately sent into a nearby optical fibre without the need for any additional coupling optics. This is a key requirement for the integration of quantum light sources into real quantum systems.
The scientists say that this streamlined process promises to simplify future integration efforts and accelerate the realisation of practical quantum photonic devices. The study’s lead author Boaz Lubotzky, a PhD student at the Racah Institute of Physics at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, said: “By overcoming key challenges associated with on-chip integration of single-photon sources, we have opened up exciting new possibilities for the development of advanced quantum technologies.”
Image credit: Hebrew University of Jerusalem



































