FBH shows tech for space and quantum applications
At ILA in Berlin, FBH will show space-qualified diode laser modules and further III-V components for satellite and quantum applications
From June 22 to 24, 2022, the Ferdinand-Braun-Institut, Leibniz-Institut für Höchst-frequenztechnik (FBH) will present semiconductors for applications in the fields of space, satellites and quantum technology at the International Aerospace Exhibition (ILA) in Berlin.
The institute covers the entire value chain – from chip design and processing to modules and systems. FBH is exhibiting its developments at the joint stand of the Berlin-Brandenburg Aerospace Alliance.
Laser systems for quantum optical experiments
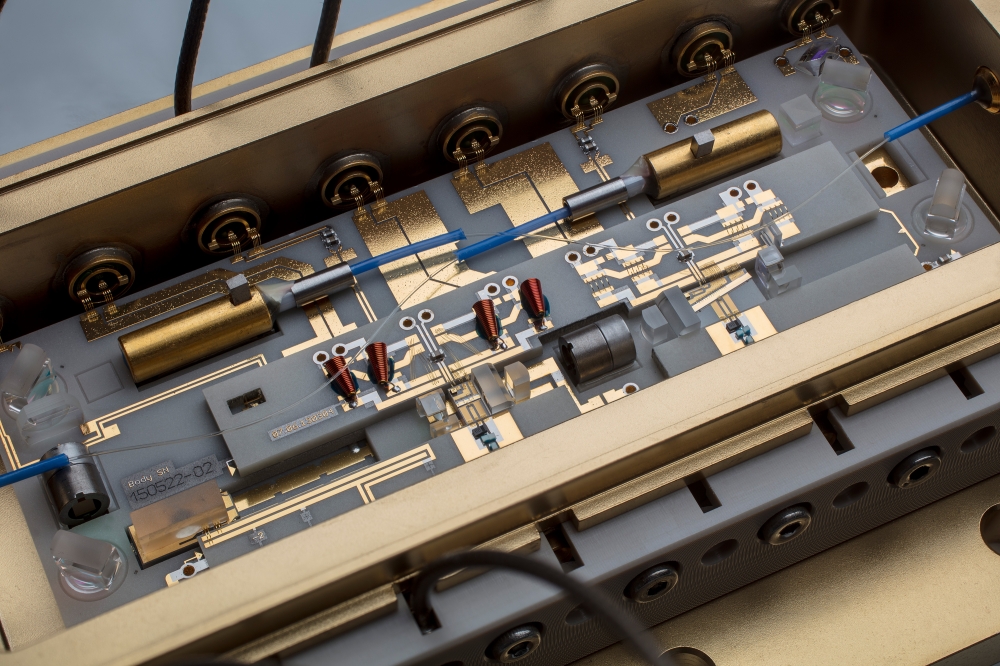
For many years, FBH has been developing and manufacturing robust and compact diode laser modules for demanding space applications. These modules have already proven their capability several times in experiments under zero gravity conditions. At the booth, the institute will show one of its 55 ultra-narrowband laser modules developed and currently manufactured for the BECCAL (Bose-Einstein Condensate – Cold Atom Laboratory) apparatus.
From 2024, they are to be used in the research facility for quantum optical experiments with ultra-cold atoms on board the International Space Station ISS. Fundamental physics questions with quantum objects are to be investigated with high precision near the absolute temperature zero (-273.15 °C).
The core elements of these and previous diode laser modules are laser diodes developed by the FBH, which are assembled together with optics and other passive elements with maximum stability and precision. The micro-integrated laser modules are based on the institute's patented MiLas® technology specially developed for use in space.
They are robust, feature small dimensions of only 125 x 75 x 23 mm³ and a low mass (750 g). At the same time, they achieve excellent output powers of > 500 mW with a narrow intrinsic linewidth < 1 kHz. In parallel, FBH is already working on an even more compact option and is currently transferring the proven concept of the hybrid Extended Cavity Diode Laser (ECDL) to a single chip.
In close collaboration with Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, such modules are also being built into compact quantum sensors and optical clocks for use in space and for industry-compatible system solutions in quantum technology. The collaborative Joint Lab presents a novel, fully autonomous frequency-stabilized laser source with integrated DFB laser diode based on the D2 transition in rubidium, operating at 780 nm.
Laser modules for satellites
Developments also include pump laser sources used in laser communication terminals for optical data transmission (EDRS) and for satellite monitoring of the greenhouse gas methane (MERLIN). Each FBH module for MERLIN is equipped with two high-power laser half-bars providing 130 W of pulsed emission at 808 nm wavelength.
Their reliability over the entire mission lifetime has been confirmed through independent testing. Newly developed DBR laser array modules offer both low noise and high reliability thanks to an integrated chip-level Bragg reflector. The modules have been qualified for more than 15 years of continuous operation. This makes them suitable as flight hardware, for example for pumping Nd:YAG lasers used for optical data communication.
Components for satcoms and sensors
Due to their high radiation hardness and their capability of switching at high frequencies, gallium nitride (GaN) switching transistors are particularly suitable for power conditioning in satellites. FBH’s 10 A/400 V aluminum nitride power core with GaN power transistors in half-bridge configuration minimizes parasitic inductances and capacitances of the switching cell.
Power switch, gate driver and DC link capacitors are hetero-integrated in an extremely compact manner, and heat is efficiently dissipated through the aluminum nitride substrate. In this way, the switching times of the power cell could be halved compared to a conventional design with discrete devices. High switching frequencies combined with high converter efficiency are the prerequisite for power converters with particularly high power-density. A decisive advantage, since weight is key in space. Only recently, it was possible to further reduce the size of a converter – while maintaining the same performance.
Energy efficiency and dissipated power are critical issues also for the RF transmitters in satellites. Thus, FBH develops concepts for envelope tracking – a well-proven technique for increasing the efficiency of RF solid-state power amplifiers.



































