Photonic Accelerator Could Increase Computation Speed and Efficiency
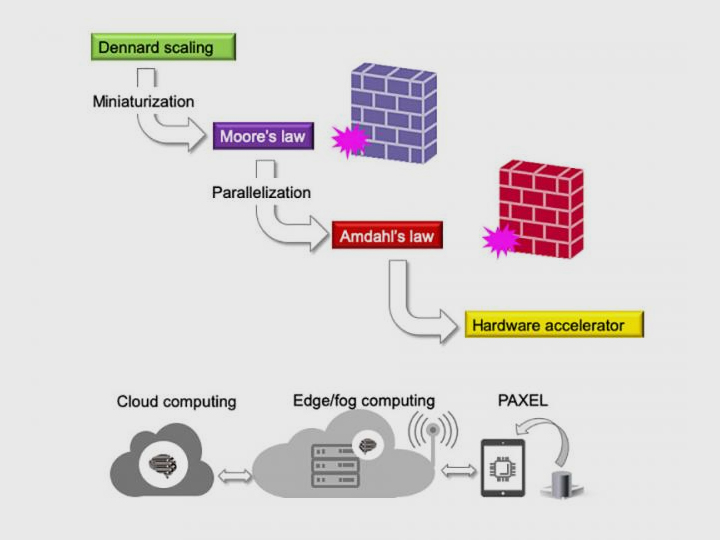
Researchers in Japan have developed a type of processor called PAXEL, a device that can potentially bypass Moore’s law and increase the speed and efficiency of computing. PAXEL uses light for the data transport step in integrated circuits. This image shows the evolution and bottlenecks of electronic integrated circuits for digital computing, and cloud versus fog computing and use of PAXEL devices. Courtesy of Ken-ichi Kitayama.
A new photonic integrated circuit device, developed by researchers in Japan, can be placed at the front end of a digital computer and optimized to perform specific functions with less power consumption than is needed for fully electronic devices. This photonic accelerator, called PAXEL, is a special class of processor that can process images or time-serial data either in an analog or digital fashion on a real-time basis. PAXEL is distinct from electronic accelerators in that the target information is optically sensed and processed.
Semiconductor transistors are the basis for most integrated electronic circuits, but they are limited by Moore’s law, which says the number of microprocessor chips on a single electronic circuit will double every two years. It is possible to partially overcome the limitations of Moore’s law by using parallel processing; however, this approach does not work for every application.
PAXEL uses nanophotonics for the data transport step in integrated circuits, and photons are not subject to Moore’s law. Nanophotonics devices operate at the speed of light and can carry out computations by varying light intensity.
The researchers considered different PAXEL architectures for a variety of uses including artificial neural networks, reservoir computing, pass-gate logic, decision-making, and compressed sensing. One possible application of PAXEL is in fog computing. This is similar to cloud computing but uses servers near the “ground” where the originating event occurs. A compact PAXEL attached to a tablet or other hand-held device could detect signals and transmit the information through a 5G wireless link to nearby fog computing resources for data analysis.
The team hopes that its work prompts others to pioneer new frontiers of photonics for data processing and that PAXEL eventually becomes an intelligent mobile tool in daily life. Applications of this new technology are possible in many areas, including medical and veterinary point-of-care testing, diagnostics, drug and food testing, and biodefense. As more household and business devices are connected through the web, better computing capacity, including data transport with higher energy efficiency, will be needed.
The research took place in Japan at the Graduate School for the Creation of New Photonics Industries in Hamamatsu; the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology in Koganei; the NTT Basic Research Laboratories in Atsugi; the University of Tokyo; Kyushu University in Fukuoka; and Saitama University in Saitama.
The research was published in APL Photonics (www.doi.org/10.1063/1.5108912).



































