Sound offers new directions in integrated photonics
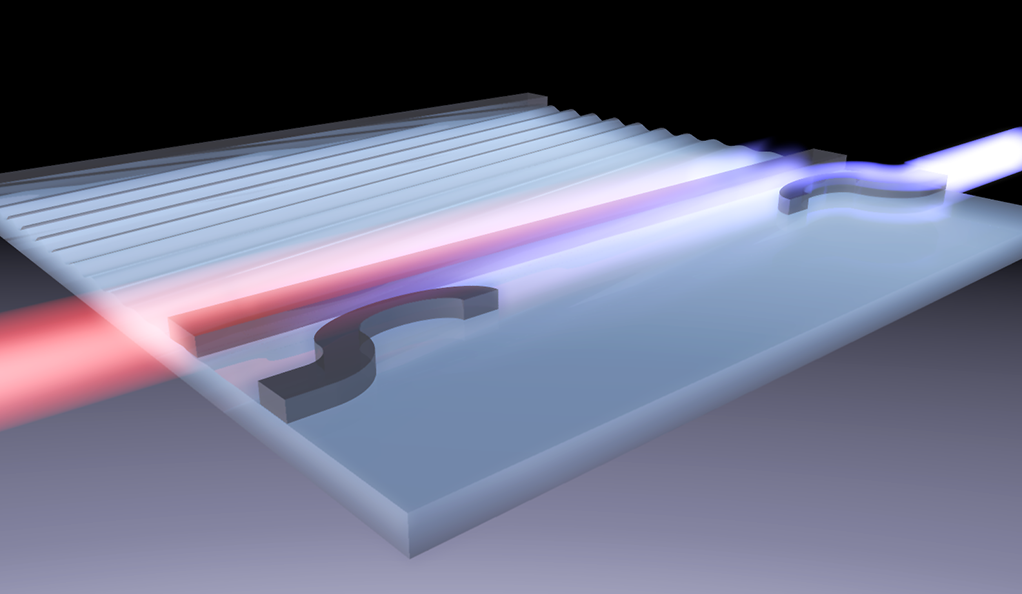
Yale scientists have demonstrated a new method to control the behaviour of light on a silicon chip "” specifically, its direction "” by using sound waves. This discovery appears in Sept. in the journal Nature Photonics.
For decades, researchers have tried to adapt widely used optical technologies "” including lasers, transmitters, and receivers "” to microchip-based devices. "The field of integrated photonics offers potential breakthroughs for applications ranging from energy-efficient communications to precision sensing and quantum information," explained Peter Rakich, an associate professor of applied physics at Yale, who led the research team. "It's very exciting because we're already seeing these technologies used in practical commercial systems."
A major challenge is the lack of chip-scale technologies that can produce so-called non-reciprocal operations. These include isolators, which are "diodes" for light that permit transmission in only one direction, and circulators, which separate forward- and backward-moving light waves into separate channels. Eric Kittlaus, the study's first author, said, "These kinds of devices are technologically important because they allow us to control and route light on a chip. For example, if we have an on-chip laser and some of its emitted light gets reflected back inside, this can severely impact the device's performance. Using an isolator, we can make sure that light is only allowed to exit our laser."
In most materials, light behaves the same whether it is traveling forward or backward. Existing approaches to produce commercial benchtop optical isolators typically involve synthetic garnet crystals interfaced with permanent magnets. However, when building on-chip devices, neither exotic crystals nor magnetic fields are readily available.
As a result, alternate proposals have sought to use electrical or acoustic control of chip-based optical circuits to demonstrate non-reciprocal light propagation. Thus far, these promising approaches have been hindered by problems such as excess loss of light signal or working only for light that is a single color.
By coupling light and sound on a silicon chip, Rakich's team demonstrated that traveling ultrasound waves can produce non-reciprocal propagation for light over wavelength ranges 100 times greater than previously observed, and with practically no excess loss of the light signal. The same system has another benefit: The sound waves themselves were created using light, allowing the researchers to control the shape and direction of the ultrasound emission at will. This extra "knob" allows the same device to operate on light signals of practically any color, according to the researchers.
"Beyond the practical uses, it's an example of very interesting and non-intuitive physics "” seeing these different parts come together is very elegant," Kittlaus said.
Nils Otterstrom, one of the paper's co-authors said, "We're thrilled by the scientific and technological implications of this work. Not only does this structure allow us to explore new physical phenomena, but it also represents a significant milestone towards the realization of practical chip-scale isolator and circulator technologies, one of the most significant remaining challenges facing integrated photonics."
Additional co-authors from the Yale Department of Applied Physics include graduate students Prashanta Kharel and Shai Gertler.



































