400G CWDM8 optics for next generation data center networks
The drive for 400G
- Data center networking bandwidth requirements continue to grow at an explosive rate, in line with the growth of consumer and business cloud services. To support new application needs, hyperscale cloud service providers are gearing up to deploy next-generation 12.8T switch and other networking equipment, and driving the interconnect speeds between switches to 400 Gb/s. To enable the 400G data rate transition, new optics interface technology is needed that meets the low-power, high-density, and low-cost requirements of Ethernet networking infrastructure deployments in hyperscale cloud data centers. The 400G CWDM8 industry MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) Group was formed by several key optics, component, and system companies with a common interest in tackling this challenge by defining new open optical interface specifications designed specifically for 400G interoperability in data center applications. Current members of the MSA Group include Accton, AOI, Barefoot Networks, Credo, H3C, Hisense, Innovium, Intel, Keysight, Mellanox, MACOM, NeoPhotonics, Nokia/ALU, and Rockley Photonics.
CWDM8 requirements for data center applications
- To meet the needs of next-generation data centers, the CWDM8 MSA group had to define 400G optical interface specifications that meet several key data center networking requirements:
Compatibility with networking equipment and next-generation module form factors
- CWDM8 optical modules can be implemented with standard IEEE CDAUI-8 8x50G PAM4 electrical inputs, making them fully compatible with next-gen networking silicon supporting 400G, including 12.8T and 14.4T Ethernet switches and other 50G/lane networking equipment
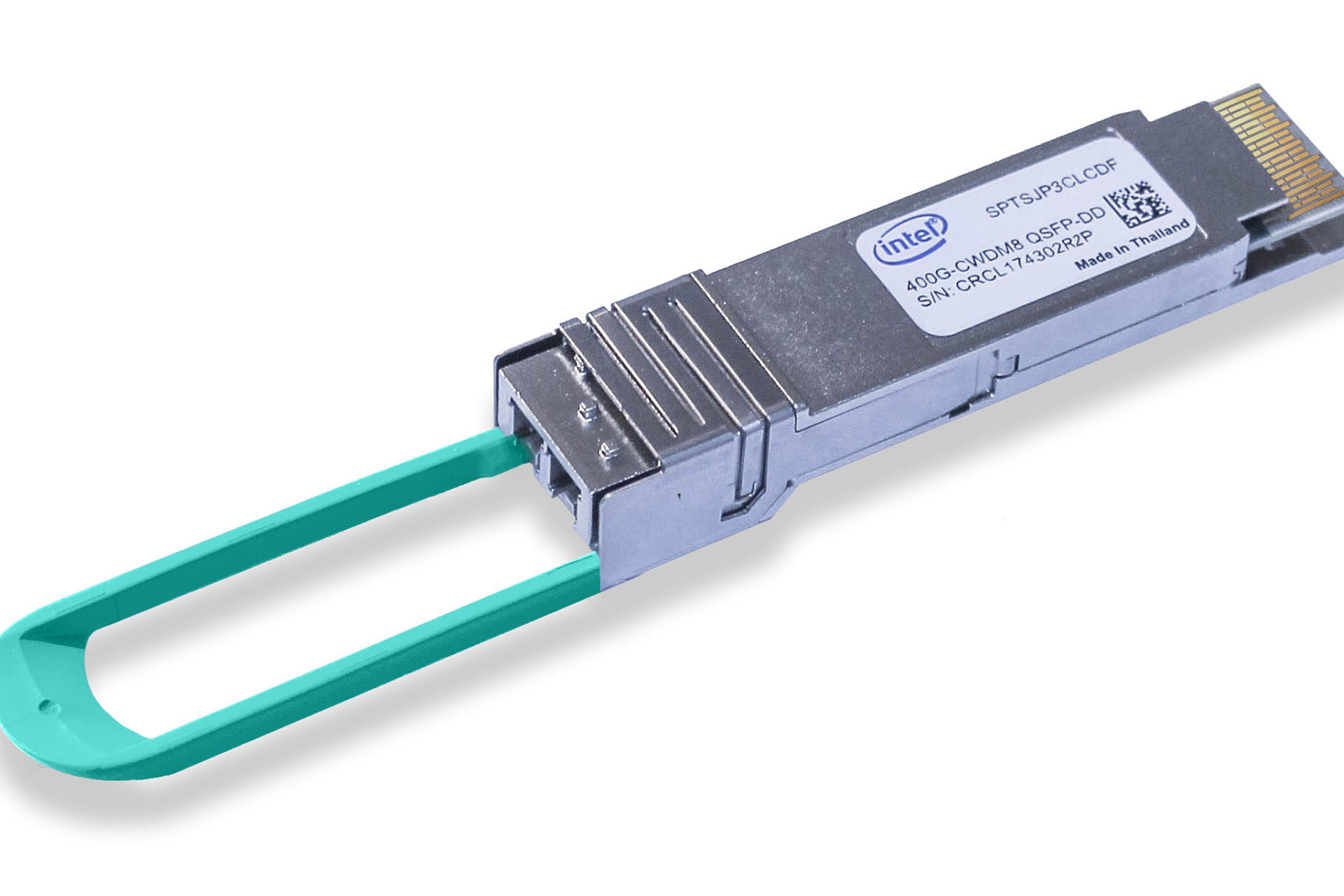
- CWDM8 can also be implemented in any of the 400G module form factors currently being considered in the industry including QSFP-DD, OSFP, and COBO, providing up to 36x400G bandwidth density per line card.
Full multi-vendor interoperability over an optical link
- The CWDM8 MSA defines two optical interface specifications, both designed to run over standard duplex single mode fiber and connectors. The 2 km specification is targeted at data center backbone applications inside large data centers, and the 10 km specification is targeted at data center campus and other applications between buildings. The MSA group has done the technical due diligence to write specifications that will ensure worst-case interoperability between any two compliant CWDM8 optical modules.
Support for low-power implementations
- The CWDM8 optical interface is designed so that the optical module can operate without an internal thermoelectric cooler, for significantly reduced power dissipation and cost.
Proven technology with ability to scale
- The CWDM8 interface uses proven NRZ technology to enable solutions with higher yield, lower cost, and faster time to volume, ensuring that 400G optics is ready for the scale and quick ramp requirements of hyperscale data center deployments. NRZ transmission has been successfully proven out over multiple previous generations of optics deployment, and is well suited to channels with higher bandwidth and lower SNR (which is typically the case for optical channels), as NRZ signaling avoids the significant SNR penalty from multi-level PAM4 signaling.
50Gbd NRZ optical eye diagram
50Gbd PAM4 optical eye diagram
Path to future interfaces beyond 400G
- The CWDM8 technology approach for 400G also lays the groundwork for future 800G interfaces for 25.6T switches, as PAM4 can be added in the future to the native 50Gbd interface to enable 8x100G PAM4 optical links. This growth/upgrade path for the 400G and 800G data rate transitions allows the more proven and higher-margin 50G/lane NRZ technology to be deployed in the 400G generation while allowing more time for maturity of 100G/lane PAM4 before deployment in the 100G/lane switch generation with additional optical component improvements.
CWDM8 status and next steps
After technical discussions, the CWDM8 MSA Group has released both the 2 km and 10 km 400G MSA optical interface specifications, both of which are available at www.cwdm8-msa.org. 400G optics products based on the CWDM8 MSA will be available soon and will help enable the 400G interconnect transition in data centers in 2018-19 and beyond.



































