Quantum dots amplify light with electrical pumping
LANL team takes critical step towards solution-processed laser diodes
Los Alamos National Lab (LANL) scientists have shown that they can successfully amplify light using electrically excited films of chemically synthesised quantum dots. They reported their results in Nature Materials.
"Optical gain with electrically excited quanum dots is now a reality," said Victor Klimov, head of the quantum dot team at Los Alamos. "We have been working to develop new lasing media, using chemically synthesised quantum dots, although it had been widely believed that quantum dot lasing with electrical stimulation is simply impossible," he said. "By using our specially designed dots, we can avoid energy losses created by Auger recombination."
These results demonstrate the feasibility of a new generation of highly flexible, electrically pumped lasers processible from solutions that can complement or even eventually displace existing laser diodes fabricated using more complex and costly vacuum-based epitaxial techniques.
These prospective devices can enable a variety of applications, from RGB laser modules for displays and projectors, to multi-wavelength micro-lasers for biological and chemical diagnostics.
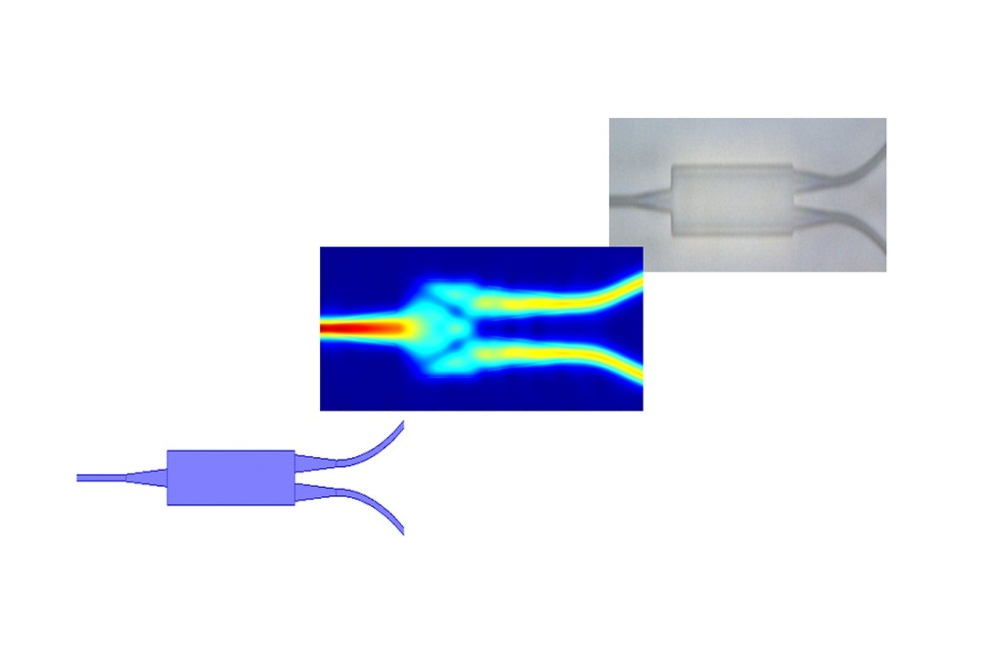
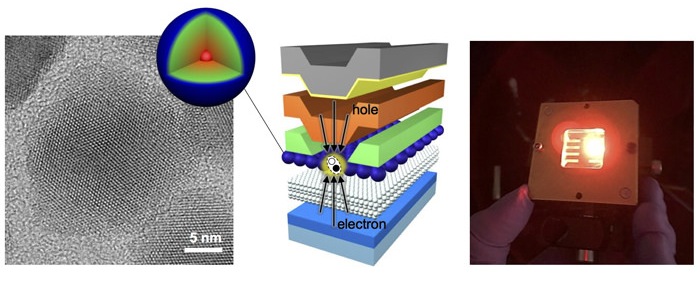
(The picture above shows a transmission electron microscopy image of the improved quantum dot and its representation (left), the schematic of the device which illustrates "current-focusing" idea (middle), and the device under operation (right)).
Designer dots with no heat loss
The key property of the novel quantum dots, underlining the success of the conducted study, is a carefully engineered particle interior in which the material's composition is continuously varied along a radial direction.
This approach eliminates sharp steps in the atomic composition which would normally trigger Auger recombination. As a result, the engineered quantum dots feature nearly complete suppression of Auger effect's heat loss, and this allows for redirecting the energy released by the electrical current into the light-emission channel instead of wasteful heat.
The team originally discovered the lasing effect in semiconductor nanocrystals in 2000. In these proof-of-principle experiments, reported in the journal Science, the quantum dots were stimulated with very short (femtosecond) laser pulses used to outcompete optical gain decay caused by the Auger process.
Short optical gain lifetimes create an especially serious problem in the case of electrical pumping, which is an inherently slow process as electrons and holes are injected into the quantum dot one-by-one.
Staying focused
Another important element of this work is a special 'current-focusing' device architecture which allows the high current densities necessary for achieving optical gain. The method used by Los Alamos researchers was to taper one of the charge-injection electrodes, limiting the size of the current-conducting area to less than 100 microns. Using this strategy, they were able to produce current concentration sufficient to reach the regime of light amplification without damaging either the dots or the injection layers.
'Optical Gain in Colloidal Quantum Dots Achieved with Direct-Current Electrical Pumping' by Jaehoon Lim et al; Nature Materials.