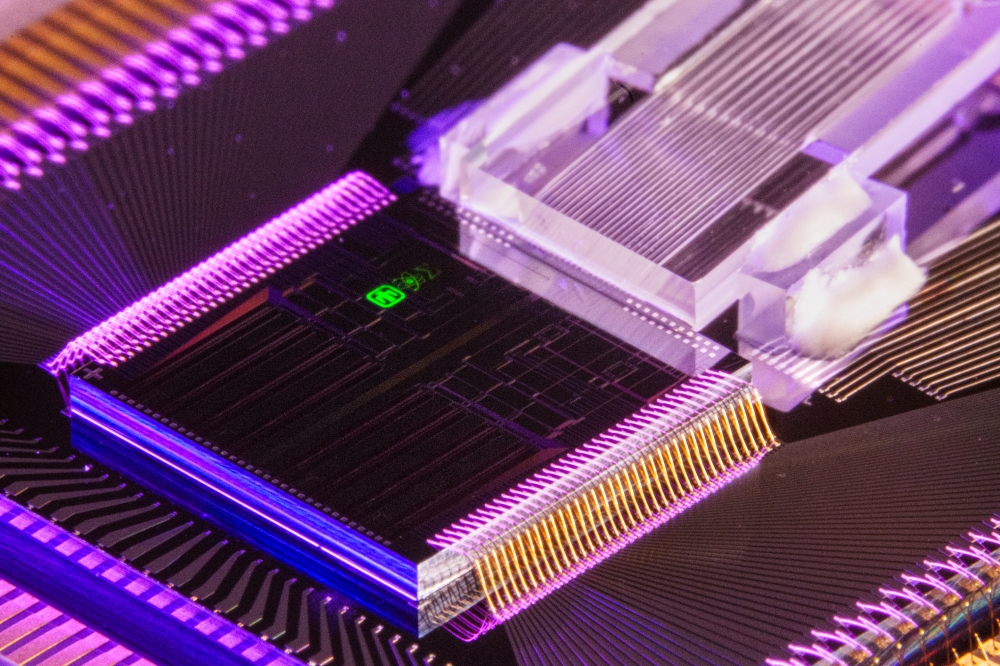
UCSB to use photonics circuits for brain imaging
Team proposes miniaturised multiphoton microscope based on cutting-edge photonic integrated circuits to enable live animal imaging
A multidisciplinary team of researchers, including UC Santa Barbara (UCSB) scientists John Bowers, Michael Goard and Luke Theogarajan, has been awarded $9 million from the US National Science Foundation (NSF) to develop and widely share state-of-the-art optical brain-imaging techniques.
The group of neuroscientists, electrical engineers, molecular biologists, neurologists, bioengineers and physicists was recognised for its collaborative NEMONIC (NExt generation MultiphOton NeuroImaging Consortium) project, which pushes the boundaries of brain imaging.
The NEMONIC group uses light to measure brain activity. The wavelengths of light that the human eye processes do not pass through brain tissue easily. Instead, they bounce off the surface of the brain, the skull or the skin and appear opaque, limiting the human ability to see internal brain activity.
However, longer wavelengths of light can pass through brain tissue unobstructed. NEMONIC employs strategic combinations of these longer wavelengths to reach deeper into the brain and image the activity of cells that have been engineered to glow when stimulated.
The three-part NEMONIC project first will develop new, streamlined multiphoton imaging approaches. Second, the team will widely share the newly engineered technologies and strategies to promote the free and productive acquisition and exchange of data across the international neuroscience community. Lastly, the NEMONIC team will capitalise on UCSB's expertise in photonics and super-resolution techniques to push the boundaries of what is possible with optical neuroimaging.
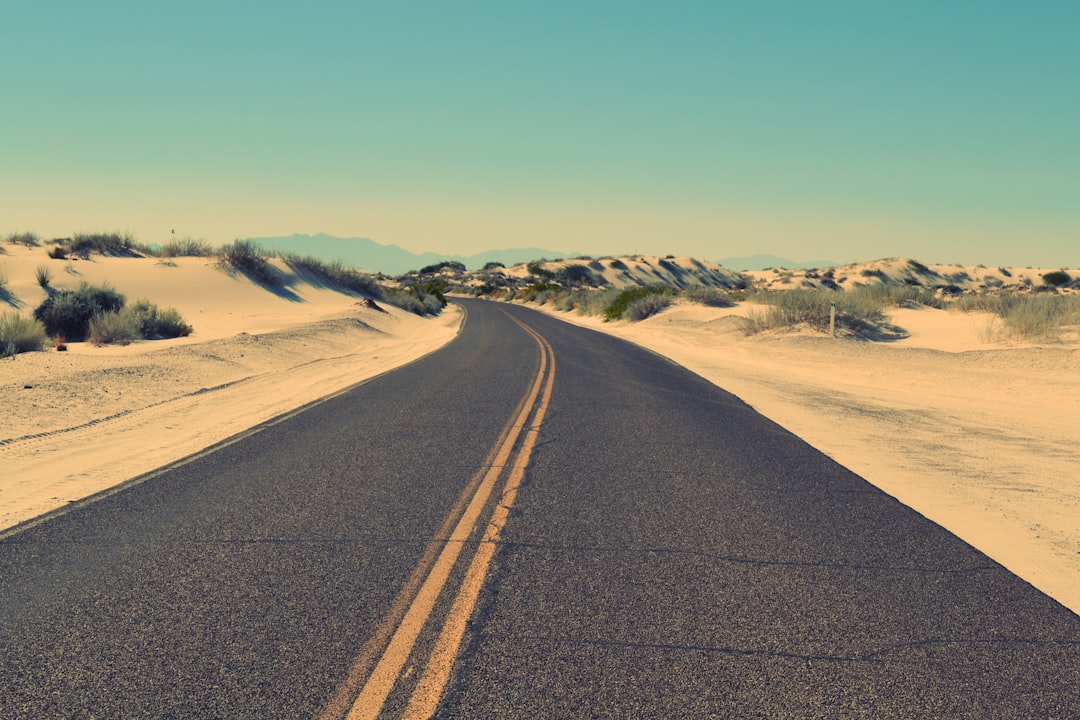
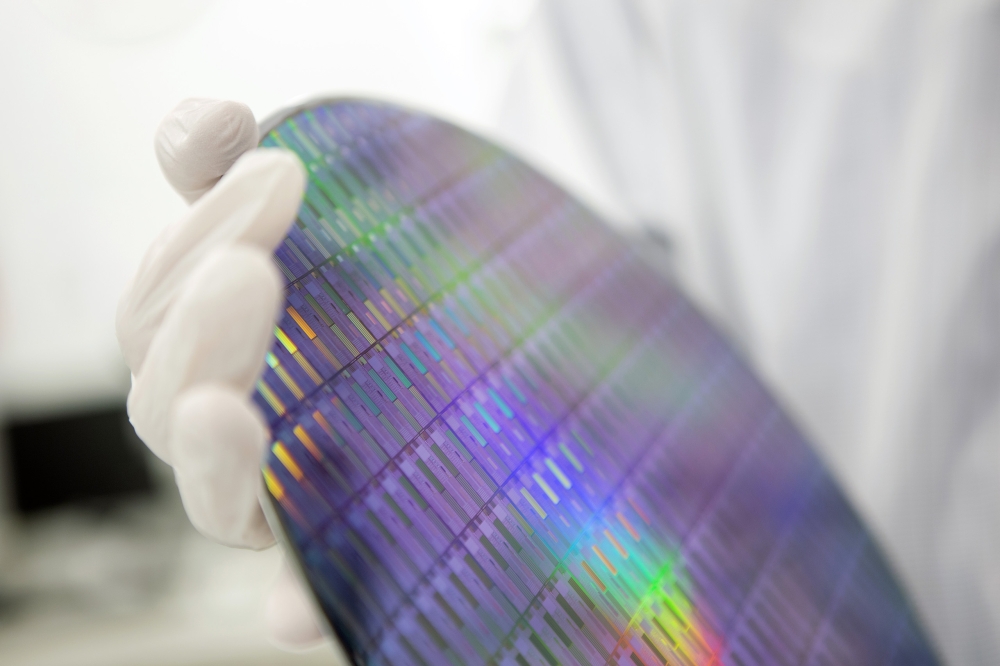
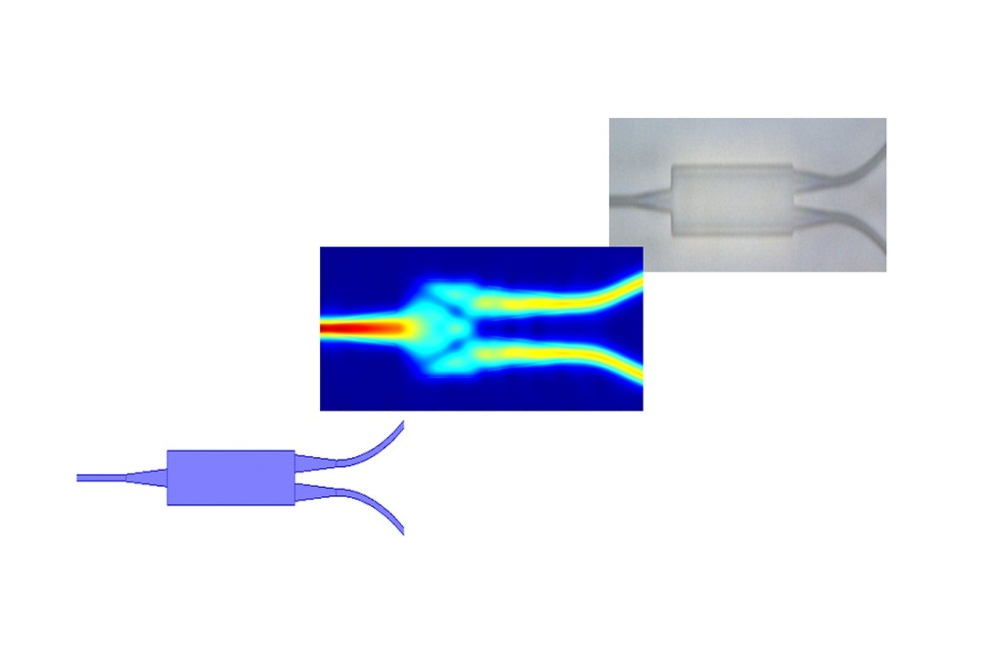
"Current methods of peering into the brain use bulky expensive lasers to generate the narrow femtosecond pulses needed for multiphoton imaging," said NEMONIC team member Theogarajan, a professor in UCSB's Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. "We are proposing a miniaturised multiphoton microscope based on cutting-edge photonic integrated circuits developed at UCSB, enabling live animal imaging and making multiphoton imaging cheaper."
"Labs around the world are imaging the brains of a range of animal species, but multiphoton microscopy systems are expensive and require significant expertise to build and use," said Goard, an assistant professor in UCSB's Department of Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology and in its Department of Psychological & Brain Sciences. "We want to make the multiphoton imaging process easier, cheaper and more robust, so we can all combine and analyze our data more effectively."
"The limit to understanding the brain is no longer the ability to store, process and analyse data," said B.N. Queenan, associate director of the UCSB Brain Initiative. "The fundamental barrier is the ability to see the brain in action. As neuroscientists, we would love to watch brain cells going about their daily business. We want to record all the cells all the time, but that's just not possible with the existing technologies. Fundamentally, we need to invent new ways of seeing what brains are up to."
"Bringing light and electronics together is what UCSB is known for," said Rod Alferness, dean of the UCSB College of Engineering. "UCSB is the West Coast headquarters of the American Institute for Manufacturing Integrated Photonics (AIM Photonics), where we integrate light-based approaches with electronics to invent and manufacture new telecommunication technologies. We are thrilled that UCSB can now deploy its particular talents in integrated photonic technology toward the brain."
To remove the technological bottlenecks to understanding the mind and the brain, the federal government launched the BRAIN (Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies) Initiative in 2013. As the name implies, the initiative is focused on developing new tools and strategies to image, map, diagnose, understand and repair the brain.
The NSF is one of the federal agencies leading the BRAIN Initiative. This year, the NSF gave 17 Next Generation Networks for Neuroscience (NeuroNex) awards to support the development of new experimental tools, theoretical frameworks and computational models that can be widely shared to advance neuroscience research. With this award, UCSB is now a designated NeuroNex Neurotechnology Hub, making it a critical part of the national neuroengineering network.