Nanoparticle arrays can switch from mirror to window

Latest research at Imperial College could help scientists create materials whose optical properties can be changed in real time
By finely tuning the distance between nanoparticles in a single layer, researchers at Imperial College London have made a filter that can change between a mirror and a window.
The development could help scientists create special materials whose optical properties can be changed in real time. These materials could then be used for applications from tuneable optical filters to miniature chemical sensors.
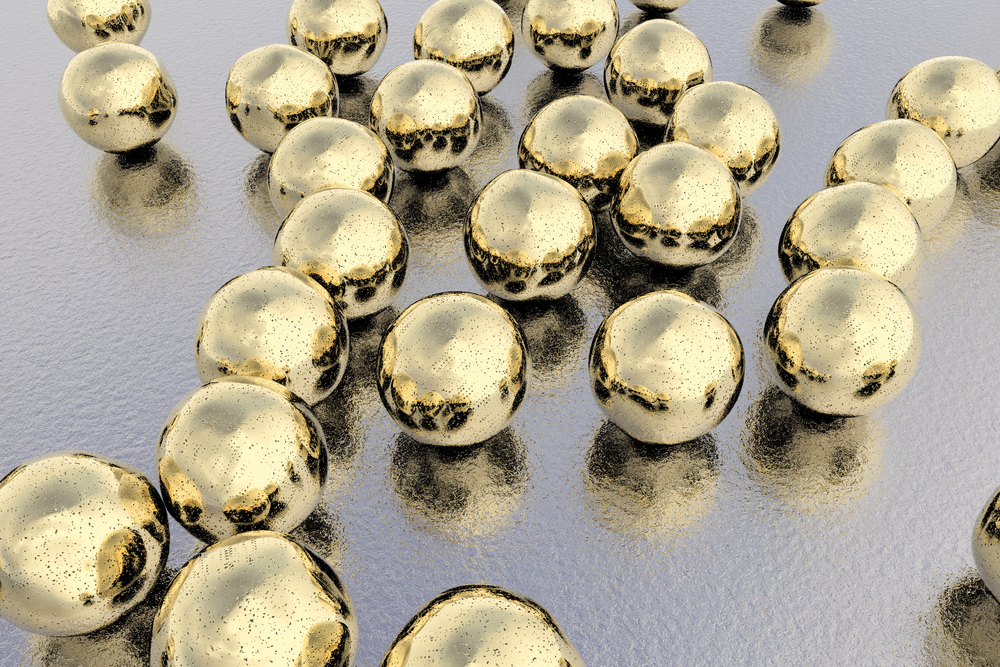
Creating a 'tuneable' material - one which can be accurately controlled - has been a challenge because of the tiny scales involved. In order to tune the optical properties of a single layer of nanoparticles - which are only tens of nanometres in size each - the space between them needs to be set precisely and uniformly.
To form the layer, the team of researchers from Imperial College London created conditions for gold nanoparticles to localise at the interface between two liquids that do not mix. By applying a small voltage across the interface, the team have been able to demonstrate a tuneable nanoparticle layer that can be dense or sparse, allowing for switching between a reflective mirror and a transparent surface. The research is published in Nature Materials.
The video above shows the system in action. The layer first acts as a window onto a £10 note below, and then reflects the £1 coin above when a voltage is applied.
Study co-author Joshua Edel, from the Department of Chemistry at Imperial, said: "It's a really fine balance - for a long time we could only get the nanoparticles to clump together when they assembled, rather than being accurately spaced out. But many models and experiments have brought us to the point where we can create a truly tuneable layer."
The distance between the nanoparticles determines whether the layer permits or reflects different wavelengths of light. At one extreme, all the wavelengths are reflected, and the layer acts as a mirror. At the other extreme, where the nanoparticles are dispersed, all wavelengths are permitted through the interface and it acts as a window.
In contrast to previous nanoscopic systems that used chemical means to change the optical properties, the team's electrical system is reversible.
Study co-author Alexei Kornyshev, from the Department of Chemistry at Imperial, said: "Finding the correct conditions to achieve reversibility required fine theory; otherwise it would have been like searching for a needle in a haystack. It was remarkable how closely the theory matched experimental results."
Co-author Anthony Kucernak, also from the Department of Chemistry, commented: "Putting theory into practice can be difficult, as one always has to be aware of material stability limits, so finding the correct electrochemical conditions under which the effect could occur was challenging."
Kornyshev added: "The whole project was only made possible by the unique knowhow and abilities and enthusiasm of the young team members, including Yunuen Montelongo and Debarata Sikdar, amongst others who all have diverse expertise and backgrounds."