Single-photon emitter holds promise for quantum info-processing
Los Alamos researchers produces first known material capable of single-photon emission at room temperature and at telecommunications wavelengths
Los Alamos National Laboratory researchers have produced the first known material capable of single-photon emission at room temperature and at telecommunications wavelengths, using chemically functionalised carbon nanotubes. The research was reported in Nature Photonics.
These quantum light emitters are important for optically-based quantum information processing and information security, ultrasensitive sensing, metrology and imaging needs and as photon sources for quantum optics studies.
"By chemically modifying the nanotube surface to controllably introduce light-emitting defects, we have developed carbon nanotubes as a single photon source, working toward implementing defect-state quantum emitters operating at room temperature and demonstrating their function in technologically useful wavelengths," said Stephen Doorn, leader of the project at Los Alamos and a member of the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies (CINT).
"Ideally, a single photon emitter will provide both room-temperature operation and emission at telecom wavelengths, but this has remained an elusive goal. Up to now, materials that could act as single photon emitters in these wavelengths had to be cooled to liquid helium temperatures, rendering them much less useful for ultimate applications or scientific purposes," he said.
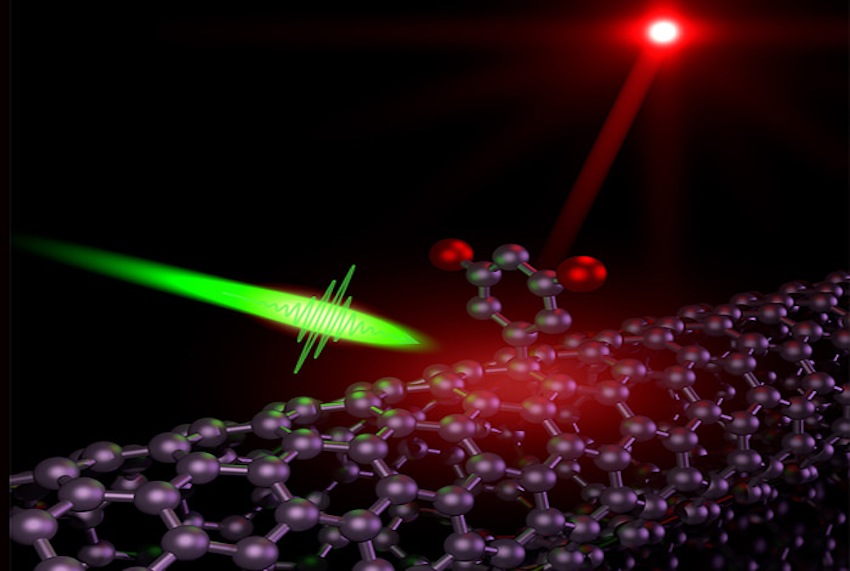
A critical breakthrough in the CINT nanotube work was the ability of the team to force the nanotube to emit light from a single point along the tube, only at a defect site. The key was to limit defect levels to one per tube. One tube, one defect, one photon. . . . By emitting light only one photon at a time, one can then control the photons' quantum properties for storage, manipulation and transmission of information.
The CINT researchers were able to attain this degree of control using diazonium-based chemistry, a process they used to bind an organic molecule to the nanotube's surface to serve as the defect.
The diazonium reaction chemistry allowed a controllable introduction of benzene-based defects with reduced sensitivity to natural fluctuations in the surrounding environment. Importantly, the versatility of the diazonium chemistry also permitted the researchers to access the inherent tunability of nanotube emission wavelengths.
The wavelengths (or colour) of the photons produced in most other approaches had been too short for telecommunications applications, where photons need to be efficiently manipulated and transported within optical circuits. The team found that by choosing a nanotube of appropriate diameter, the single photon emission could be tuned to the essential telecom wavelength region.
The functionalised carbon nanotubes have significant prospects for further development, Doorn noted, including advances in functionalisation chemistry; integration into photonic, plasmonic and metamaterials structures for further control of quantum emission properties; and implementation into electrically driven devices and optical circuitry for diverse applications.
Funding: This research was funded in part by the Laboratory Directed Research and Development (LDRD) program and performed in part at the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies, a DOE Office of Science User Facility.
'Tunable Room-Temperature Single-Photon Emission at Telecom Wavelengths from sp3 Defects in Carbon Nanotubes'; Nature Photonics (2017)