Photonics Breakthrough paves way for improved wireless communication systems

Researchers at the University of Sydney's Australian Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology achieve radio frequency signal control at sub-nanosecond time scales on a chip-scale optical device.
Researchers from the ARC Centre for Ultrahigh bandwidth Devices for Optical Systems (CUDOS) in the University of Sydney's Australian Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology have made a breakthrough achieving radio frequency signal control at sub-nanosecond time scales on a chip-scale optical device.
Radio frequency (RF) is a particular range of electromagnetic wave frequencies, widely used for communications and radar signals. The work should impact the current wireless revolution.
CUDOS and School of Physics PhD candidate at the University of Sydney, lead author Yang Liu, said the new research that could unlock the bandwidth bottleneck faced by wireless networks worldwide was undertaken at the headquarters of the Australian Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology (AINST), the $150m Sydney Nanoscience Hub.
"Nowadays, there are 10 billion mobile devices connected to the wireless network (reported by Cisco last year) and all require bandwidth and capacity," Mr Liu said.
"By creating very fast tunable delay lines on chip, one eventually can provide broader bandwidth instantaneously to more users."
"The ability of rapidly controlling RF signal is a crucial performance for applications in both our daily life and defence."
"For example, to reduce power consumption and maximise reception range for future mobile communications, RF signals need to achieve directional and fast distributions to different cellular users from information centres, instead of spreading signal energy in all directions."
The lack of the high tuning speed in current RF technique in modern communications and defence, has motivated the development of solutions on a compact optical platform. These optical counterparts had been typically limited in performance by a low tuning speed on the order of milliseconds (1/1000 of a second) offered by on-chip heaters, with side effects of fabrication complexity and power consumption.
"To circumvent these problems, we developed a simple technique based on optical control with response time faster than one nanosecond: a billionth of a second "“ this is a million times faster than thermal heating," said Mr Liu.
CUDOS Director and co-author Professor Benjamin Eggleton, who also heads the Nanoscale Photonics Circuits AINST flagship, said the technology would not only be important for building more efficient radars to detect enemy attacks but would also make significant improvements for everyone.
"Such a system will be crucial not only to safeguard our defence capabilities, it will also help foster the so-called wireless revolution "“ where more and more devices are connected to the wireless network," Professor Eggleton said.
"This includes the internet of things, fifth generation (5G) communications, and smart home and smart cities."
"Silicon photonics, the technology that underpins this advance, is progressing very quickly, finding applications in datacentres right now."
"We expect the applications of this work will happen within a decade in order to provide a solution to the wireless bandwidth problem. We are currently working on the more advanced silicon devices that are highly integrated and can be used in small mobile devices," Professor Eggleton said.
David Marpaung, Benjamin Eggleton, Yang Liu and Amol Choudhary inside the Sydney Nanoscience Hub, pointing at a thumbnail-size chip being evaluated in the broadband microwave testbed.
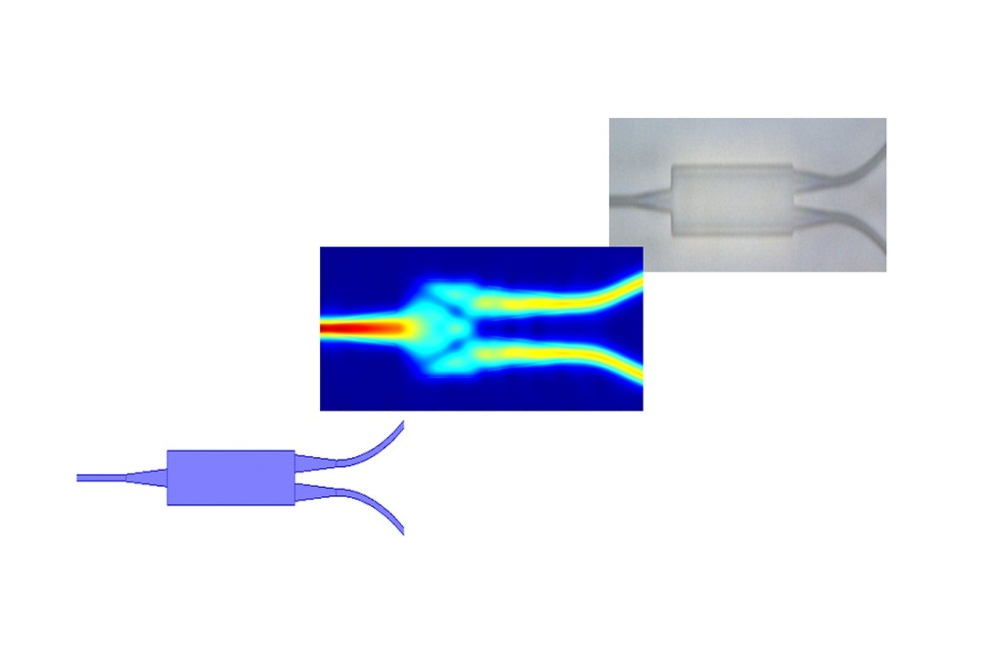
By optically varying the control signal at gigahertz speeds, the time delay of the RF signal can be amplified and switched at the same speed, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Schematic illustration of the fast control of RF signals
The research builds on research supported by the Australian Research Council through CUDOS, a Centre of Excellence.
Mr Liu and fellow researchers Dr Amol Choudhary, Dr David Marpaung and Professor Benjamin Eggleton achieved this on an integrated photonic chip, paving the way towards ultrafast and reconfigurable on-chip RF systems with unmatched advantages in compactness, low power consumption, low fabrication complexity, flexibility and compatibility with existing RF functionalities.
The research builds on research supported by the Australian Research Council through CUDOS, a Centre of Excellence.